
You can see where each actor is involved within the entire process (and where they're excluded). Take a look at our use case diagram guide to learn more about the benefits of use case diagrams and the shapes involved.Īs you can see from the examples below, use cases are represented by oval shapes, and the lines then show at which point an actor participates and interacts with their corresponding use case. With a UML use case diagram, you can create a broad, high-level view of the relationship between use cases, actors involved, and systems being performed. UML Component Diagram for Online Shopping (Click on image to modify online) UML Component Diagram for Library Management System (Click on image to modify online) UML Component Diagram for ATM (Click on image to modify online)

Take a look at our examples below, and dive into our component diagram guide to become more familiar with component diagrams.

The connected circles, or “lollipop” symbols, represent realization relationships within the systems. The component diagram examples below show the structural relations between components in an online shopping system, library management system, and an ATM system. Diagrams are structured this way so that the components can be easily replaced when needed. The components that make up this type of diagram are modular parts of the system that are inherently replaceable.
SAMPLE SEQUENCE DIAGRAM FOR NETWORK SOFTWARE
Both component and class diagrams display the structural relationship of software systems and their elements however, component diagrams generally simplify the interactions within more complex systems. UML Class Diagram for Online Shopping (Click on image to modify online) UML Class Diagram for Domain Models (Click on image to modify online) UML Class Diagram for Library Management Systems (Click on image to modify online)Ĭomponent diagrams in UML are very similar to class diagrams. From there, additional UML symbols are used to model the various interactions and objects involved within the process. In our examples below, you'll find that each class shape is labeled with its name in the first row, the second row displays each attribute of the class on a separate line, and the third row displays each operation on a separate line. Software engineers and business professionals often choose class diagrams to map the structure of particular systems because they clearly display the various classes, attributes, operations, and relationships between objects. The class diagram is one of the most commonly used diagrams in UML, as explained in depth in our guide on class diagrams. and I would also consider drawing the scenario (use case) from different perspectives with different focus using different diagrams, mainly I would think about drawing an overview diagram using the language "BPMN 2.Class diagram templates Component diagram templates Object diagram templates Activity diagram templates Sequence diagram templates Use case diagram templates Class diagram templates (2) and I would also draw the "queue changed" signal broadcasted by the queue upon receiving new token same as (3) and yes I would represent the "listening" process as loop box on its own lifeline as you suggest (1) yes I would create a lifeline representing the queue Agents in the neighborhood then might "smell" it and metabolize further. then I would also model the central "tuple space" or the central multi-agent coordination structure as dumb unconscious, but living actor which would metabolize some scent molecules whenever it "eats" something through the membrane.
SAMPLE SEQUENCE DIAGRAM FOR NETWORK HOW TO
If you mean how to draw sequence diagram for something similar to this scenario.
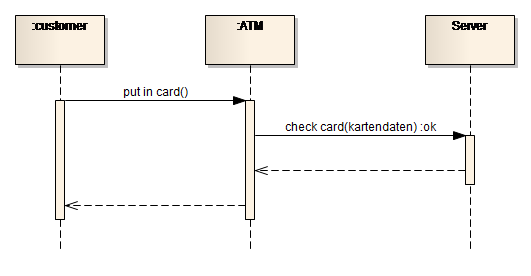
To indicate that the consumer is always listening, I have ended the diagram again with a listen call that hasn't returned. This is under the assumption that the producer and consumer execute asynchronously. One back to the producer to indicate completion of the insert call, and the other to the consumer to indicate completion of the listen call. At this point, I would use two return arrows. As the queue is an important component in the sequence you are presenting, it should most definitely be present with a lifeline.Īs the consumer explicitly listens for events from the queue, I would start the diagram with the listen call from the consumer to the queue.Īfter that, the producer can insert its event into the queue (possibly with an indication that a considerable amount of time can elapse between the listen call and the insertion of the event).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
